- Independent testing
Envirolyte systems and generated solutions (anolyte and catolyte) have been put through extensive series of independent tests and on-site trials including hospitals, breweries, water systems and agricultural environments.
- Safer world
Being environmentally friendly, completely safe, non-toxic and non-irritant Anolyte is welcome where traditional chemicals fail to produce the desired results or can't be applied at all.
- Better alternative
The conclusions prove that Anolyte being a low-cost and powerful disinfectant is set to become the preferred solution for many sterilisation, disinfecting and water purification procedures.
I. Antibacterial activity
RESULT
The product under test: “Anolyte” demonstrated bactericidal activity for hygienic handrub disinfection (≥ 5 log reduction), according to the EN 13727:2012+A2:2015, at 201 °C, under clean conditions when used at concentration:
250ppm hypochlorous acid for 60 seconds contact time using as test organisms the reference strains:
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli K12 and Enterococcus hirae.
II. sporicidal activity
RESULT
The product under test: “Anolyte” demonstrated yeasticidal activity for hygienic handrub disinfection (≥ 4 log reduction) according to EN 13624:2013, at 201 °C, under clean conditions when used at concentration:
250ppm hypochlorous acid for 60 seconds contact time using as test organism the reference strain: Candida albicans
III. virusidal activity
RESULT
The antiviral activity of the product " ANOLYTE" against the Adenovirus type 5, Poliovirus type 1 and Murine norovirus was tested according to the EN 14476 standard: “Chemical disinfectants and antiseptics - Quantitative suspension test for the evaluation of virucidal activity in the medical area- test method and requirements (Phase2/Step1).” According to the EN 14476 standard a product has antiviral activity when a reduction of at least 4 lοg of the virus is observed.
The product " ANOLYTE" in 1:1 dilution, demonstrated:
• a ≥4 log reduction of the Adenovirus type 5 (ATCC VR-5) after 1 min contact time in the presence of 0.3 g/L BSA, at 20oC
• a ≥5.4 log reduction of the Poliovirus 1 Sabin strain, LSc-2ab (WHO) after 1 min contact time, respectively in the presence of 0.3 g/L BSA, at 20oC
• a ≥4.2 log reduction of the Murine Norovirus (Strain S99 Berlin) after 1 min contact time in the presence of 0.3 g/L BSA, at 20oC
The product demonstrated antiviral activity against the non-enveloped DNA adenovirus, the non-enveloped RNA poliovirus and the non-enveloped RNA murine norovirus. According to the EN 14476 standard, products that have antiviral activity against the adenovirus, the poliovirus and the murine norovirus are considered active against all viruses.
Original documents can be provided upon request along with the equipment.
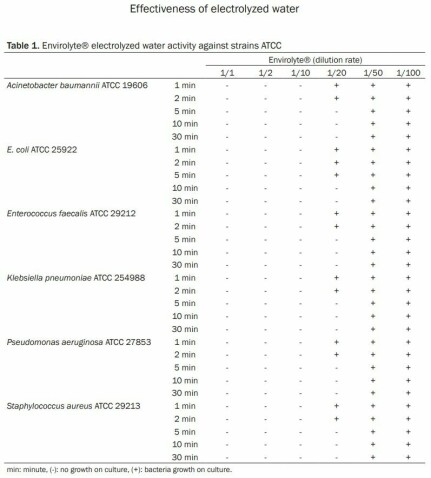
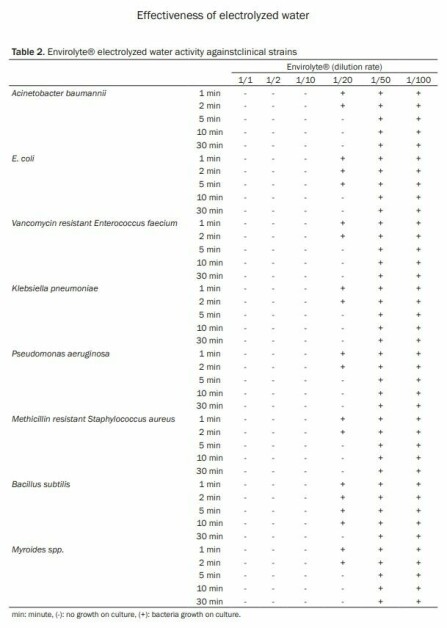
An ınvestigation into the in-vitro effectiveness of electrolyzed water (anolyte or HCLO) against various microorganisms
Keramettin Yanik1, Adil Karadag1, Nevzat Unal2, Hakan Odabasi1, Saban Esen3, Murat Gunaydin4
Departments of 1Medical Microbiology, 3Infectious Diseases and Medical Microbiology, Ondokuz Mayis University, Medical Faculty, Samsun, Turkey; 2Adana Numune Education and Research Hospital Laboratory of Microbiology Adana, Turkey; 4Department of Medical Microbiology, Istanbul University, Cerrahpasa Medical Faculty, Istanbul
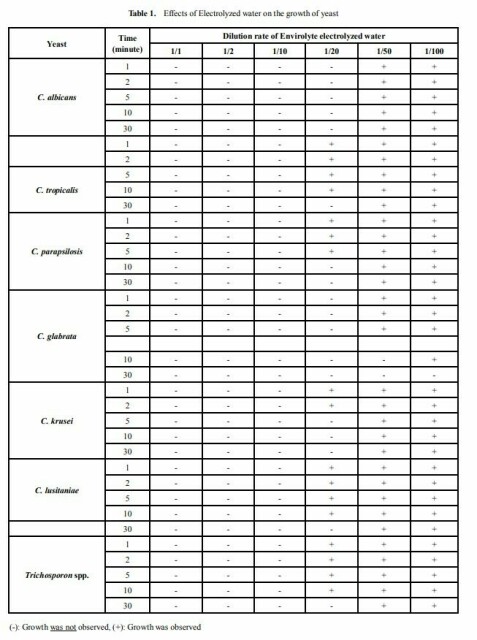
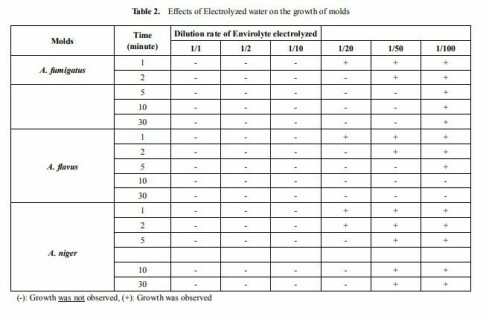
Analysis of in Vitro Efficiency of Electrolyzed Water (anolyte or HCLO) Against Fungi Species Frequently Detected in Nosocomial Infections
Nevzat Ünal1, Adil Karadağ2, Keramettin Yanık2,*, Kemal Bilgin3, Murat Günaydın4, Asuman Birinci2
Adana Numune Education and Research Hospital, Laboratory of Microbiology, Adana, Turkey
Ondokuz Mayis University, Medical Faculty, Department of Medical Microbiology, Samsun, Turkey
Ondokuz Mayis University, Vocational High School Health Services, Samsun, Turkey
Istanbul University, Cerrahpasa Medical Faculty, Department of Medical Microbiology, Istanbul, Turkey,